My research objective is to assist individuals in making informed human capital decisions, champion the cause of marginalized and low-income groups, empowering them to unleash their full potential, and ultimately contribute to the cultivation of social equity. —— Yu Zhao
Education and Labor Economics
Demystifying College Costs Through Behavioral Nudges: Experimental Evidence from China.
Click to Expand Full Abstract.
Abstract: There has been a global trend of rapid college tuition increases, which often come with diverse financial aid packages. How (low-income) students behaviorally respond to these changes in their college choices remains as an open question. In a preregistered field experiment with 5,000 low-income college applicants in China, we examine six major behavioral barriers that may prevent students from correctly understanding the cost-benefit tradeoff of college attendance and making optimal college choices. Those barriers include biased belief, information friction, administrative burden, framing, overconfidence, and social image. In a pilot experiment with 560 college applicants in the summer of 2023, results show that the amalgamation of nudging information has led to a statistically significant increase in the likelihood of students from economically disadvantaged regions opting for universities in larger cities. However, we find large heterogeneities in the treatment effects, yielding more favorable outcomes for students with higher educational aspirations, stronger family backgrounds, and those initially hesitant to attend universities in large cities. Causal Forests analysis further indicates that intervention impacts vary based on students' anticipated tuition costs and personality traits. The results of the main experiment, which will be available shortly, will provide novel experimental evidence for improving financial aid policies for low-income students across the world.
🌻
Information for Vision: Experimental Evidence on Nudging Low-income Students to Wear Eyeglasses.
Jiusheng Zhu , Xinjie Zhang , Yu Zhao , Xiaoyang Ye .
Click to Expand Full Abstract.
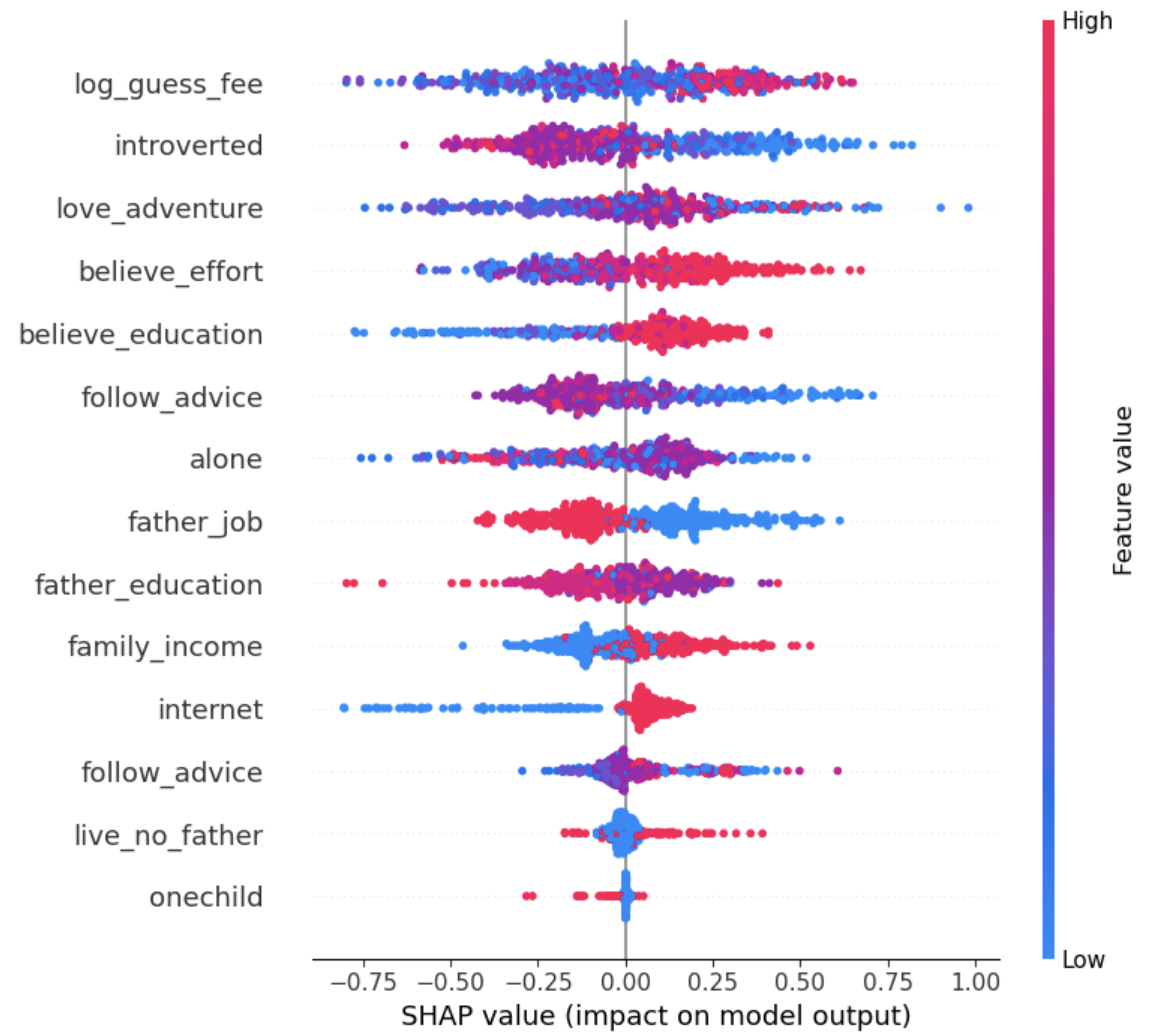
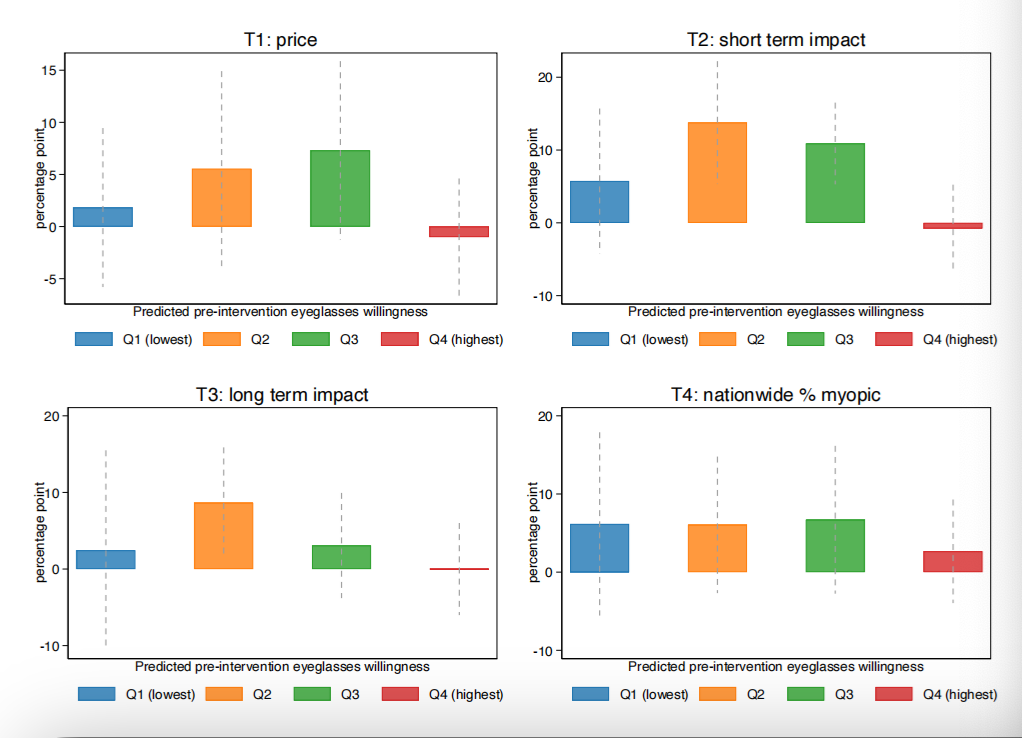
Abstract: This study uses a randomized experiment to examine the effectiveness of informational nudges about eyeglasses on middle-school students’ decisions to purchase glasses when needed. With a sample of 8,808 low-income middle school students in China, the experimental results show that the short-term impact of wearing glasses on academic achievement (vs. long-term impact or social norm) is the most effective information for students. We also find heterogeneity in baseline belief, peer effects, as well as in how students with different characteristics respond to various types of information. Cost-benefit analysis demonstrates efficacy and cost-effectiveness of nudges in improving academic outcomes. Our results provide novel evidence of the importance of precise, personalized information nudges in improving students' educational input and academic achievement.
🌻
The Long-term Influence of Education Resources Allocation on the Migration:Evidence from the China’s Rural School Consolidation Policy. [PDF]
Yu Zhao
, Hui Du
, Rui Li
, Guangsu Zhou
.
Accepted by Journal of Asian Economics.
Click to Expand Full Abstract.
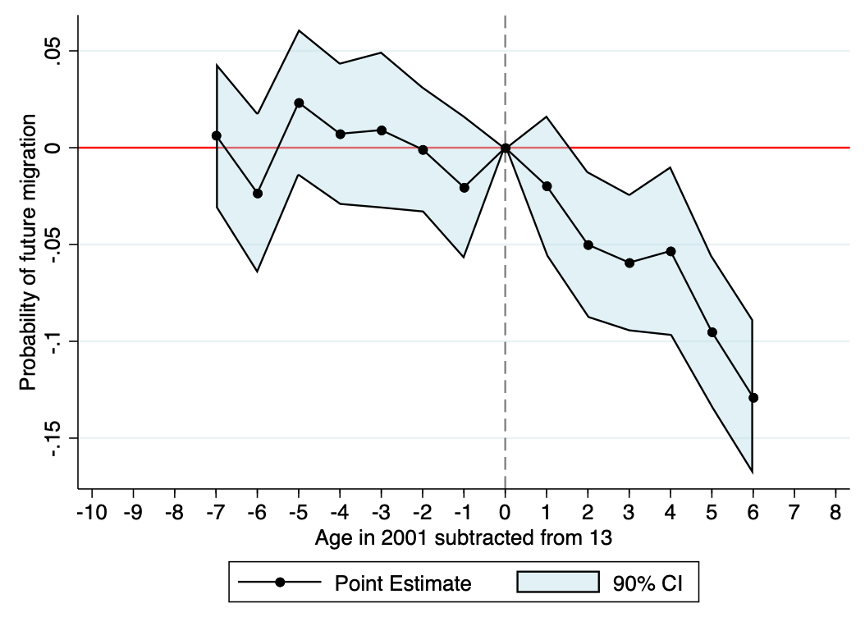
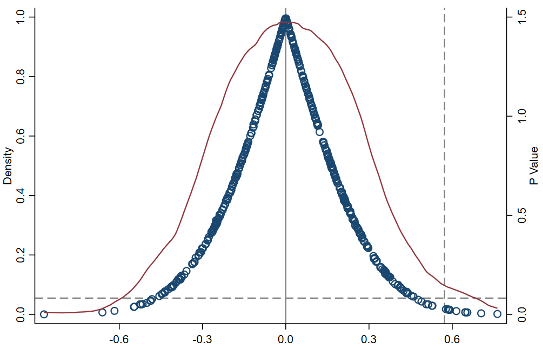
The experiences of student life can have lasting impacts on an individual’s future outcomes. We take the policy of the Rural Primary School Consolidation Program (RPSCP) in 2001 as a quas-inatural experiment, and comprehensively examine the long-term impact of this policy on students’ migration decisions in the future. We find that the RPSCP policy has a persisting negative impact on rural students’ future migration, with a more pronounced effect among girls and younger students. Mechanism analysis suggests that the RPSCP can hinder the process of human capital accumulation, thereby reducing the likelihood of migration. Further investigation highlights that school consolidation not only affects students’ career choices, but also has a profound impact on household registration conversion and settlement intentions in other regions.
🌻
Yu Zhao , Hui Du , Rui Li , Guangsu Zhou .
Click to Expand Full Abstract.
Abstract: We take the implementation of "China’s New Labor Contract Law" (NLCL) in 2008 as a quasi-natural experiment, and apply the Difference-in-Differences method to assess the impact of the policy on human capital investment in migrant workers’ families. Our analysis reveals that the NLCL leads to a significant increase in education expenditure among migrant workers’ families. Heterogeneity analysis shows that the effect is more pronounced in families with higher education levels, families with only one child, and families that belong to medium income levels. Mechanism analysis suggests that the NLCL increases the likelihood of migrant workers receiving pension and medical insurance, thereby reducing the associated risks and burdens for families and ultimately boosting education spending. The NLCL not only protects the labor rights and interests of vulnerable groups like migrant workers, but also has significant implications for enhancing human capital investments, promoting social mobility, and achieving shared prosperity.
🌻
Agricultural Economics and Rural Development
Yu Zhao , Jianjun Zhu . Xinjiang State Farms Economy, 2021.
Click to Expand Full Abstract.
Abstract: 2020 is the year to win the battle against poverty in an all-round way. The focus of poverty governance will shift to relatively invisible poverty. As an important indicator of poverty prevention and control, vulnerability to poverty is of great significance for establishing a long-term mechanism to solve relative poverty. This paper empirically analyzed the impact of financial literacy on the poverty vulnerability of rural residents by using the 2015 China Household Financial Survey(CHFS)data. The results show that financial literacy has a significant negative impact on the poverty vulnerability of rural households, and the improvement of financial literacy is helpful to reduce the poverty vulnerability of rural households. Further research shows that the proportion of risk assets, off-farm entrepreneurship and insurance purchase play an intermediary role in the process of financial literacy affecting poverty vulnerability, and financial literacy can reduce poverty vulnerability by influencing the proportion of risk assets, encouraging off-farm entrepreneurship and insurance purchase.
🌻
Research on the Impact of Farmland Rights Confirmation upon Rural Labor to Migrant to Work. [PDF]
Yu Zhao , Jianjun Zhu . Rural Economy and Technology, 2019.